|
Automatic evaluations and transformations
Evaluation for exact and machine-number values of arguments
For the exact argument 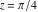 , Mathematica returns an exact result. , Mathematica returns an exact result.
For a machine‐number argument (numerical argument with a decimal point), a machine number is also returned.
The next inputs calculate 100‐digit approximations at 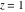 and and 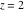 . .
Within a second, it is possible to calculate thousands of digits for the cosecant function. The next input calculates 10000 digits for 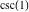 and analyzes the frequency of the digit and analyzes the frequency of the digit 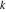 in the resulting decimal number. in the resulting decimal number.
Here is a 50‐digit approximation to the cosecant function at the complex argument 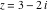 . .
Mathematica automatically evaluates mathematical functions with machine precision, if the arguments of the function are numerical values and include machine‐number elements. In this case only six digits after the decimal point are shown in the results. The remaining digits are suppressed, but can be displayed using the function InputForm.
Simplification of the argument
Mathematica knows the symmetry and periodicity of the cosecant function. Here are some examples.
Mathematica automatically simplifies the composition of the direct and the inverse cosecant functions into its argument.
Mathematica also automatically simplifies the composition of the direct and any of the inverse trigonometric functions into algebraic functions of the argument.
In cases where the argument has the structure 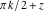 or or 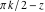 , and , and 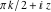 or or 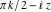 with integer with integer 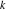 , the cosecant function can be automatically transformed into trigonometric or hyperbolic cosecant or secant functions. , the cosecant function can be automatically transformed into trigonometric or hyperbolic cosecant or secant functions.
Simplification of combinations of cosecant functions
Sometimes simple arithmetic operations containing the cosecant function can automatically generate other equal trigonometric functions.
The cosecant function arising as special cases from more general functions
The cosecant function can be treated as a particular case of some more general special functions. For example, 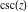 appears automatically from Bessel, Struve, Mathieu, Jacobi, hypergeometric, and Meijer functions for appropriate values of their parameters. appears automatically from Bessel, Struve, Mathieu, Jacobi, hypergeometric, and Meijer functions for appropriate values of their parameters.
|