|
Calculating the series expansion of a sine function to hundreds of terms can be done in seconds. Mathematica comes with the add‐on package DiscreteMath`RSolve` that allows finding the general terms of series for many functions. After loading this package, and using the package function SeriesTerm, the following 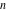 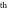 term of term of 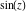 can be evaluated. can be evaluated. This result can be checked by the following process. Mathematica can evaluate derivatives of the sine function of an arbitrary positive integer order. Mathematica can calculate finite symbolic sums that contain the sine function. Here are some examples. Mathematica can calculate infinite sums that contain sine function. Here are some examples. Mathematica can calculate some finite symbolic products that contain the sine function. Here are two examples. Mathematica can calculate a huge number of doable indefinite integrals that contain the sine function. Here are some examples. Mathematica can calculate wide classes of definite integrals that contain the sine function. Here are some examples. Mathematica can calculate limits that contain the sine function. Here are some examples. The next inputs solve two equations that contain the sine function. Because of the multivalued nature of the inverse sine function, a message indicates that only some of the possible solutions are returned. A complete solution of the previous equation can be obtained using the function Reduce. Here are differential equations whose linear independent solutions include the sine function. The solutions of the simplest second-order linear ordinary differential equation with constant coefficients can be represented using 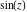 and and 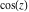 . . In the last input, the differential equation was solved for 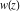 . If the argument is suppressed, the result is returned as a pure function (in the sense of the . If the argument is suppressed, the result is returned as a pure function (in the sense of the 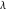 ‐calculus). ‐calculus). The advantage of such a pure function is that it can be used for different arguments, derivatives, and more. In carrying out the algorithm to solve the following nonlinear differential equation, Mathematica has to solve a transcendental equation. In doing so, the generically multivariate inverse of a function is encountered, and a message is issued that a solution branch is potentially missed. Mathematica supports the main integral transforms like direct and inverse Fourier, Laplace, and Z transforms that can give results that contain classical or generalized functions. Mathematica has built‐in functions for 2D and 3D graphics. Here are some examples.
|