|
Introduction to the Cosecant Function
Defining the cosecant function
The cosecant function is an old mathematical function. It was mentioned in the works of G. J. von Lauchen Rheticus (1596) and E. Gunter (around 1620). It was widely used by L. Euler (1748) and T. Olivier, Wait, and Jones (1881).
The classical definition of the cosecant function for real arguments is: "the cosecant of an angle 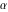 in a right‐angle triangle is the ratio of the length of the hypotenuse to the length of the opposite leg." This description of in a right‐angle triangle is the ratio of the length of the hypotenuse to the length of the opposite leg." This description of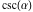 is valid for is valid for 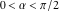 when this triangle is nondegenerate. This approach to the cosecant can be expanded to arbitrary real values of when this triangle is nondegenerate. This approach to the cosecant can be expanded to arbitrary real values of 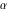 if the arbitrary point if the arbitrary point 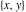 in the in the 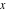 , ,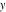 ‐Cartesian plane is considered and ‐Cartesian plane is considered and 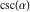 is defined as the ratio is defined as the ratio 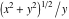 assuming that α is the value of the angle between the positive direction of the assuming that α is the value of the angle between the positive direction of the 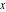 ‐axis and the direction from the origin to the point ‐axis and the direction from the origin to the point 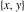 . .
Comparing the classical definition with the definition of the sine function shows that the following formula can also be used as a definition of the cosecant function:
A quick look at the cosecant function Here is a graphic of the cosecant function 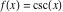 for real values of its argument for real values of its argument 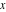 . .
Representation through more general functions
The cosecant function 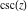 can be represented using more general mathematical functions. As the ratio of one divided by the sine function that is a particular case of the generalized hypergeometric, Bessel, Struve, and Mathieu functions, the cosecant function can also be represented as ratios of one and those special functions. Here are some examples: can be represented using more general mathematical functions. As the ratio of one divided by the sine function that is a particular case of the generalized hypergeometric, Bessel, Struve, and Mathieu functions, the cosecant function can also be represented as ratios of one and those special functions. Here are some examples:
But these representations are not very useful because they include complicated special functions in the denominators.
It is more useful to write the cosecant function as particular cases of one special function. That can be done using doubly periodic Jacobi elliptic functions that degenerate into the cosecant function when their second parameter is equal to 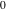 or or 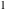 : :
Definition of the cosecant function for a complex argument In the complex 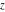 ‐plane, the function ‐plane, the function 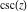 is defined using is defined using 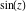 or the exponential function or the exponential function 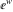 in the points in the points 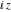 and and 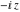 through the formula: through the formula: In the points 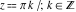 , where , where 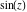 is zero, the denominator of the last formula equals zero and is zero, the denominator of the last formula equals zero and 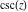 has singularities (poles of the first order). has singularities (poles of the first order). Here are two graphics showing the real and imaginary parts of the cosecant function over the complex plane.
The best-known properties and formulas for the cosecant function
Values in points
Using the connection between the sine and cosecant functions, the following table of cosecant function values for angles between 0 and 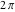 can be derived: can be derived:
General characteristics
For real values of argument 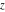 , the values of , the values of 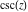 are real. are real.
In the points 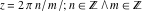 , the values of , the values of 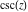 are algebraic. In several cases they can be integers are algebraic. In several cases they can be integers 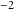 , , 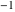 , 1, or 2: , 1, or 2:
The values of 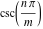 can be expressed using only square roots if can be expressed using only square roots if 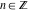 and and 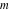 is a product of a power of 2 and distinct Fermat primes {3, 5, 17, 257, …}. is a product of a power of 2 and distinct Fermat primes {3, 5, 17, 257, …}.
The function 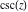 is an analytical function of is an analytical function of 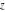 that is defined over the whole complex that is defined over the whole complex 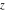 ‐plane and does not have branch cuts and branch points. It has an infinite set of singular points: ‐plane and does not have branch cuts and branch points. It has an infinite set of singular points:
(a) 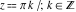 are the simple poles with residues are the simple poles with residues 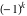 .
(b) .
(b) 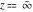 is an essential singular point. is an essential singular point.
It is a periodic function with the real period 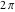 : :
The function 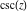 is an odd function with mirror symmetry: is an odd function with mirror symmetry:
Differentiation
The first derivative of 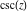 has simple representations using either the has simple representations using either the 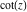 function or the function or the 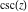 function: function:
The 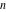 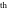 derivative of derivative of 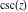 has much more complicated representations than symbolic has much more complicated representations than symbolic 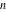 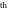 derivatives for derivatives for 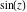 and and 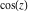 : :
where 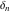 is the Kronecker delta symbol: is the Kronecker delta symbol: 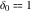 and and 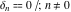 . .
Ordinary differential equation
The function 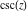 satisfies the following first-order nonlinear differential equation: satisfies the following first-order nonlinear differential equation:
Series representation
The function 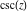 has the following Laurent series expansion at the origin that converges for all finite values has the following Laurent series expansion at the origin that converges for all finite values 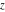 with with 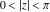 : :
where 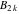 are the Bernoulli numbers. are the Bernoulli numbers.
The cosecant function 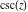 can also be represented using other kinds of series by the following formulas: can also be represented using other kinds of series by the following formulas:
Integral representation
The function 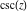 has well-known integral representation through the following definite integral along the positive part of the real axis: has well-known integral representation through the following definite integral along the positive part of the real axis:
Product representation
The famous infinite product representation for 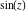 can be easily rewritten as the following product representation for the cosecant function: can be easily rewritten as the following product representation for the cosecant function:
Limit representation
The cosecant function has the following limit representation:
Indefinite integration
Indefinite integrals of expressions that contain the cosecant function can sometimes be expressed using elementary functions. However, special functions are frequently needed to express the results even when the integrands have a simple form (if they can be evaluated in closed form). Here are some examples:
Definite integration
Definite integrals that contain the cosecant function are sometimes simple. For example, the famous Catalan constant 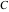 can be defined as the value of the following integral: can be defined as the value of the following integral:
This constant also appears in the following integral:
Some special functions can be used to evaluate more complicated definite integrals. For example, polylogarithmical, zeta, and gamma functions are needed to express the following integrals:
Finite summation
The following finite sums that contain the cosecant function have simple values:
Infinite summation
The following infinite sum that contains the cosecant has a simple value:
Finite products
The following finite product from the cosecant can also be represented using the cosecant function:
Addition formulas
The cosecant of a sum and the cosecant of a difference can be represented by the formulas that follow from corresponding formulas for the sine of a sum and the sine of a difference:
Multiple arguments
In the case of multiple arguments 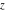 , ,  , , 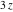 , …, the function , …, the function 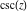 can be represented as a rational function that contains powers of cosecants and secants. Here are two examples: can be represented as a rational function that contains powers of cosecants and secants. Here are two examples:
Half-angle formulas
The cosecant of a half‐angle can be represented by the following simple formula that is valid in a vertical strip:
To make this formula correct for all complex 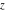 , a complicated prefactor is needed: , a complicated prefactor is needed:
where 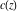 contains the unit step, real part, imaginary part, and the floor functions. contains the unit step, real part, imaginary part, and the floor functions.
Sums of two direct functions
The sum and difference of two cosecant functions can be described by the following formulas:
Products involving the direct function
The product of two cosecants and the product of the cosecant and secant have the following representations:
Inequalities
Some inequalities for the cosecant function can be easily derived from the corresponding inequalities for the sine function:
Relations with its inverse function
There are simple relations between the function 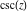 and its inverse function and its inverse function 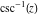 : :
The second formula is valid at least in the vertical strip 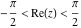 . Outside of this strip a much more complicated relation (that contains the unit step, real part, and the floor functions) holds: . Outside of this strip a much more complicated relation (that contains the unit step, real part, and the floor functions) holds:
Representations through other trigonometric functions
Cosecant and secant functions are connected by a very simple formula that contains the linear function in the argument:
The cosecant function can also be represented using other trigonometric functions by the following formulas:
Representations through hyperbolic functions
The cosecant function has representations using the hyperbolic functions:
Applications
The cosecant function is used throughout mathematics, the exact sciences, and engineering.
|