|
Operations under special Mathematica functions Series expansions Calculating the series expansion of a cosecant function to hundreds of terms can be done in seconds. Mathematica comes with the add‐on package DiscreteMath`RSolve` that allows finding the general terms of the series for many functions. After loading this package, and using the package function SeriesTerm, the following 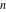  term of term of 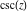 can be evaluated. can be evaluated. This result can be verified by the following process. Differentiation Mathematica can evaluate derivatives of the cosecant function of an arbitrary positive integer order. Finite products Mathematica can calculate some finite symbolic and nonsymbolic products that contain the cosecant function. Here are two examples. Indefinite integration Mathematica can calculate a huge number of doable indefinite integrals that contain the cosecant function. The results can contain special functions. Here are some examples. Definite integration Mathematica can calculate wide classes of definite integrals that contain the cosecant function. Here are some examples. Limit operation Mathematica can calculate limits that contain the cosecant function. Here are some examples. Solving equations The next inputs solve two equations that contain the cosecant function. Because of the multivalued nature of the inverse cosecant function, a printed message indicates that only some of the possible solutions are returned. A complete solution of the previous equation can be obtained using the function Reduce. Solving differential equations Here is a nonlinear first-order differential equation that is obeyed by the cosecant function. Mathematica can find the general solution of this differential equation. In doing so, the generically multivariate inverse of a function is encountered, and a message is issued that a solution branch is potentially missed. Plotting Mathematica has built‐in functions for 2D and 3D graphics. Here are some examples.
|