|
Definition of the hyperbolic cosecant function for a complex argument In the complex 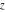 ‐plane, the function ‐plane, the function 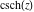 is defined by the same formula that was used to define real values: is defined by the same formula that was used to define real values: In the points 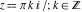 , where , where 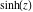 has zeros, the denominator of the last formula equals zero and has zeros, the denominator of the last formula equals zero and 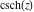 has singularities (poles of the first order). has singularities (poles of the first order). Here are two graphics showing the real and imaginary parts of the hyperbolic cosecant function over the complex plane.
|