|
On the real axis The function 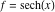 along the real axis. along the real axis. 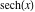 is real‐valued along the real axis that approaches is real‐valued along the real axis that approaches 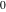 as as 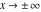 . . The absolute value and the argument of 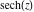 along the real axis. The left graphic shows along the real axis. The left graphic shows 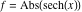 and the right graphic shows and the right graphic shows 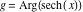 . The argument is constant. . The argument is constant. On the real axis at infinity The function 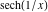 along the real axis. The left graphic shows along the real axis. The left graphic shows 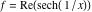 and the right graphic shows and the right graphic shows 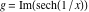 . . The absolute value and the argument of 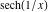 along the imaginary axis. The left graphic shows along the imaginary axis. The left graphic shows 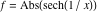 and the right graphic shows and the right graphic shows  . The argument is constant. . The argument is constant. On the imaginary axes The real part and the imaginary part of 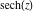 along the imaginary axis. The left graphic shows along the imaginary axis. The left graphic shows 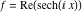 and the right graphic shows and the right graphic shows 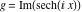 . Along the imaginary axis, . Along the imaginary axis, 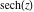 is purely imaginary and the imaginary part is oscillating and periodic with poles at is purely imaginary and the imaginary part is oscillating and periodic with poles at 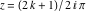 . . The absolute value and the argument of 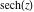 along the imaginary axis. The left graphic shows along the imaginary axis. The left graphic shows 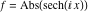 and the right graphic shows and the right graphic shows 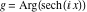 . The argument is piecewise constant. . The argument is piecewise constant. On the imaginary axis at infinity The function 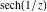 along the imaginary axis. The left graphic shows along the imaginary axis. The left graphic shows 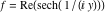 and the right graphic shows and the right graphic shows 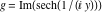 . At . At 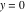 , the function , the function 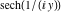 has an essential singularity. has an essential singularity. The absolute value and the argument of 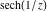 along the imaginary axis. The left graphic shows along the imaginary axis. The left graphic shows 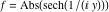 and the right graphic shows and the right graphic shows 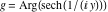 . . On the unit circle The real part and the imaginary part of 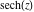 on the unit circle. The left graphic shows on the unit circle. The left graphic shows 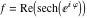 and the right graphic shows and the right graphic shows  . . The absolute value and the argument of 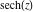 on the unit circle. The left graphic shows on the unit circle. The left graphic shows 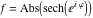 and the right graphic shows and the right graphic shows 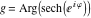 . .
|