|
The tensor functions 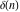 , , 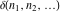 , , 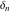 , and , and 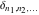 can have unit values at infinity: can have unit values at infinity:
The tensor functions 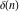 , , 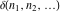 , , 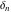 , , 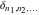 , and , and 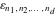 have the following values for some specialized variables: have the following values for some specialized variables:
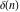 and and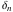 are nonanalytical functions defined over are nonanalytical functions defined over 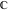 . Their possible values are . Their possible values are 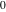 and and 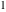 . .
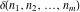 and and 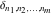 are nonanalytical functions defined over are nonanalytical functions defined over 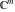 . Their possible values are . Their possible values are 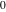 and and 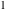 . .
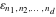 is a nonanalytical function, defined over the set of tuples of complex numbers with possible values is a nonanalytical function, defined over the set of tuples of complex numbers with possible values 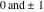 . .
The tensor functions 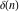 , , 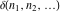 , , 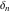 , , 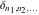 , and , and 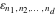 do not have periodicity. do not have periodicity.
The tensor functions 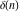 , , 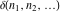 , , 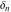 , and , and 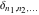 are even functions: are even functions:
The tensor functions 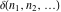 , , 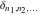 , and , and 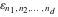 have permutation symmetry, for example: have permutation symmetry, for example:
The discrete delta function 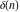 and Kronecker delta function and Kronecker delta function 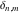 have the following integral representations along the interval have the following integral representations along the interval 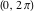 and unit circle and unit circle 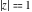 : :
The tensor functions 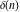 , , 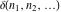 , , 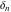 , , 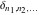 , and , and 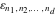 satisfy various identities, for example: satisfy various identities, for example:
The tensor functions 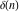 , , 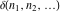 , , 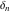 , , 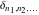 , and , and 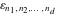 have the following complex characteristics: have the following complex characteristics:
Differentiation of the tensor functions 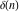 and and 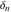 can be provided by the following formulas: can be provided by the following formulas:
Fractional integro‐differentiation of the tensor functions 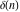 and and 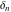 can be provided by the following formulas: can be provided by the following formulas:
Indefinite integration of the tensor functions 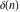 and and 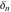 can be provided by the following formulas: can be provided by the following formulas:
The following relations represent the sifting properties of the Kronecker and discrete delta functions:
There exist various formulas including finite summation of signature 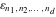 , for example: , for example:
|