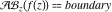
The natural boundary of analyticity of the function 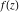 with respect to with respect to 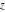 is the set boundary. is the set boundary. 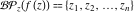
Gives a list of lists of the branch points 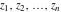 (if present, including infinity) of the function f over the complex (if present, including infinity) of the function f over the complex 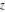 ‐plane. ‐plane. 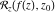
The ramification index for function 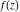 in the branch point in the branch point 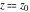 . . 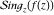
The set of poles (with their orders) and essential singularities of 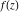 with respect to with respect to 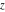 . (The order of essential singularity is ∞.) . (The order of essential singularity is ∞.) 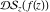
The list of the (parametrized) intervals where the function 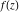 is discontinuous over the complex is discontinuous over the complex 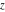 ‐plane. ‐plane.
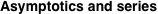
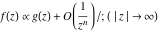
Asymptotic relation that reflects the boundedness of 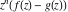 near point near point 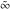 . . 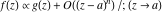
Asymptotic relation that reflects the boundedness of 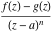 near point near point 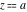 . . 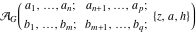
The asymptotic expansion of the function 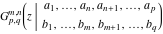 at the point at the point 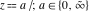 that includes that includes 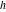 terms of the asymptotic expansions of the regular and exponential components: terms of the asymptotic expansions of the regular and exponential components: 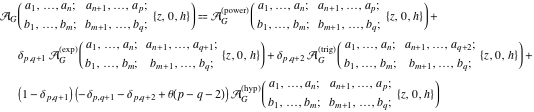 . .
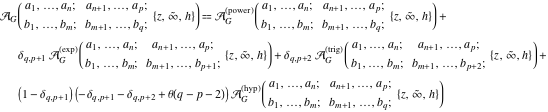 . .
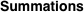
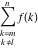
Sum of terms 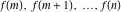 excluding the term excluding the term 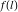 . . 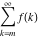
Limit of the finite sum (infinite sum): 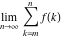 . . 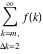
Limit of the finite sum (infinite sum): 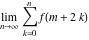 . . 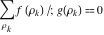
Sum over all solutions of the equation 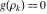 . . 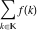
Sum over the set 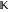 . . 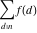
Sum of 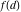 over all divisors of n. over all divisors of n. 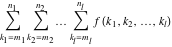
Multiple sum of function 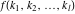 over the sets over the sets 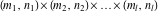 . .
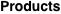
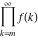
Limit of finite product 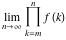 . . 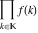
Product over set 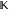 . . 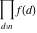
Product of 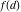 over all divisors of n. over all divisors of n.
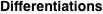
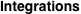
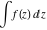
Indefinite integral (antiderivative) of function 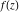 . Inverse operation to differentiation: . Inverse operation to differentiation: 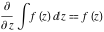 . . 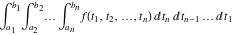
Multiple definite integral of the function 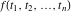 by the intervals by the intervals 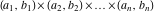 . . 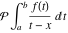
Cauchy principal value of a singular integral: 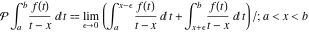 Cauchy principal value of a singular integral: 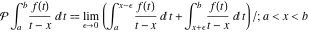 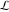
The special contour 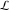 , which is used in the definition of the Meijer G function and its numerous particular cases. , which is used in the definition of the Meijer G function and its numerous particular cases. There are three possibilities for the contour 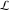 : : (i) 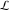 runs from γ-ⅈ ∞ to γ+ⅈ ∞ (where runs from γ-ⅈ ∞ to γ+ⅈ ∞ (where 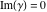 ) so that all poles of ) so that all poles of 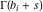 , , 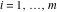 are to the left of ℒ, and all poles of are to the left of ℒ, and all poles of 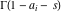 , , 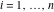 , are to the right.
This contour can be a straight line , are to the right.
This contour can be a straight line 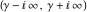 if if 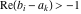 (then (then 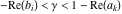 ). (In this case, the integral converges if ). (In this case, the integral converges if 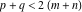 , , 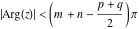 . If . If  , then , then 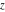 must be real and positive, and the additional condition must be real and positive, and the additional condition 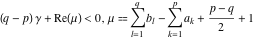 should be added. should be added. (ii) 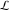 is a loop on the left side of the complex plane, starting and ending at -∞ and encircling all poles of is a loop on the left side of the complex plane, starting and ending at -∞ and encircling all poles of 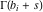 , ,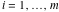 , once in the clockwise direction, but none of the poles of , once in the clockwise direction, but none of the poles of 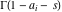 , , 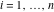 .
(In this case, the integral converges if .
(In this case, the integral converges if 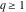 and either and either 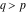 , or , or 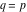 and and 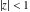 , or , or 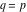 and and 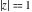 and both and both 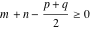 and and 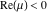 .) .) (iii) 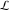 is a loop on the right side of the complex plane, starting and ending at +∞ and encircling all poles of is a loop on the right side of the complex plane, starting and ending at +∞ and encircling all poles of 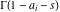 , , 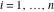 , once in the counterclockwise direction, but none of the poles of , once in the counterclockwise direction, but none of the poles of 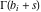 , , 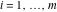 .
(In this case, the integral converges if .
(In this case, the integral converges if 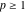 and either and either 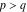 , or , or 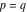 and and 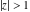 , or , or 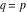 and and 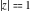 and both and both 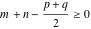 and and 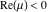 .) .)
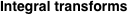
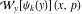
Wigner integral transform: 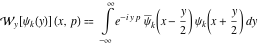 . (If this integral does not converge, the value of . (If this integral does not converge, the value of 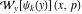 is defined in the sense of generalized functions.) is defined in the sense of generalized functions.)
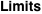
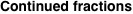
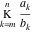
A finite continued fraction 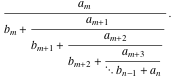 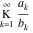
Limit of the finite continued fraction 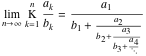 . .
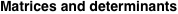
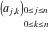
The 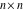 matrix with elements matrix with elements 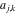 . . 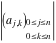
The determinant of the 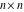 matrix with elements matrix with elements 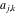 . . |